Recent Posts
-
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
So I spent some time afternoon to understand the idea behind Dijkstra. On this post, I wish to focus on the graph theoretical language and idea behind the algorithm rather than its application. I will cover the idea of crossing subsets and use path notations for graphs to formalize our idea. Suppose a graph \(G\)…
-
Grover’s Algorithm Pt 1
We have investigated methods to learn about a given mystery quantum oracle. The Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm determines whether or not the function \(f:\{0, 1\}^n \rightarrow \{0, 1\}\) is well balanced and the Bernstein-Vazirani algorithm yields the unique string that satisfies \(f(x) = 1\). The oracle presented in the Bernstein-Vazirani algorithm provides ample information about the function…
-
Probability Currents
Given a wavefunction, the observable quantity is the square of its magnitude. Wavefunctions evolve in time, and so does the distribution of the particle. For energy eigenstates, the phase of the wavefunction evolves by a speed determined by the energy. In a general state, however, the probability distribution wiggles around as all the different energy…
-
Eigenvalue Estimation Algorithm
All quantum gates correspond to a unitary operator. In fact, this implies that all the eigenvalues of a quantum gate can be described in a form of a complex exponential of the form \[\lambda \ = \ e^{i\omega}. \] Here is a proof. Let \(U\) be the unitary operator for some quantum gate and consider…
-
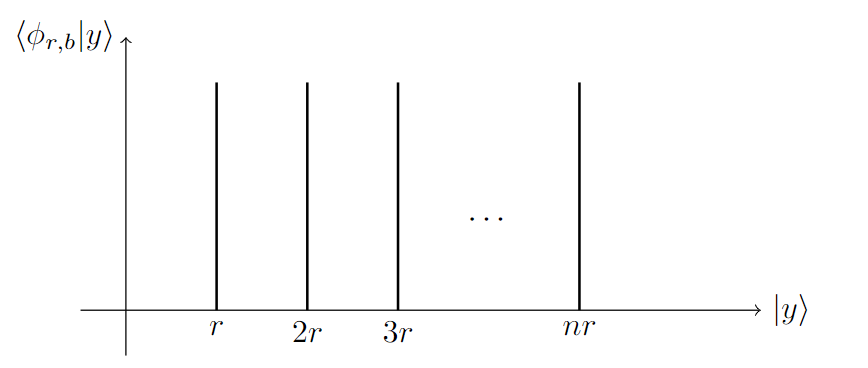
Periodic States and Period Testing
The machinery of quantum mechanics has a flavor of linear algebra and analysis. For example, quantum states exist within a Hibert space, and the Bloch sphere used to demonstrate a state of a 1-qubit system is a geometric object living in \(\mathbb R^3\). We wish to apply the abstract, continuous machinery in a discrete setting.…
-
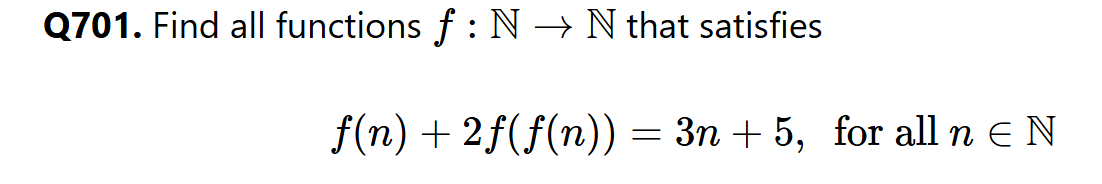
Integer Valued Functions
In this post, I wish to introduce two elementary number theory problems and their solutions. The solutions require no mathematical prerequisites other than basic understanding of logic and integer valued functions. The typical structure of these problems are as follows. A functional equation is given, along with the domain and the range of the function.…
-
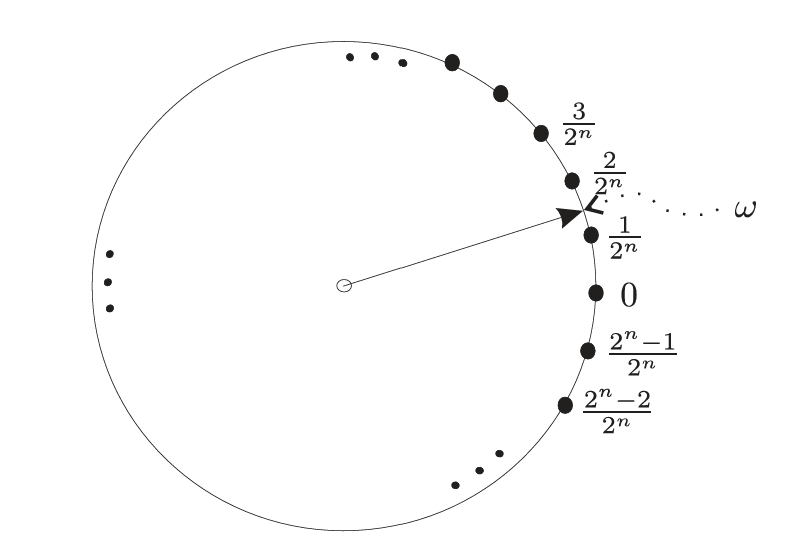
Phase Estimation for arbitrary phase
In the previous post, we explored the method of phase estimation where we recovered the phase factor \(\omega\) from the state \[ \frac 1 {\sqrt{m}}\sum_{y = 0}^{m} \exp(2 \pi i \omega y)|y\rangle \] and we demonstrated that a quantum circuit consisting of Hadamard gates and controlled rotations can recover the binary digits of \(\omega\) in…
-
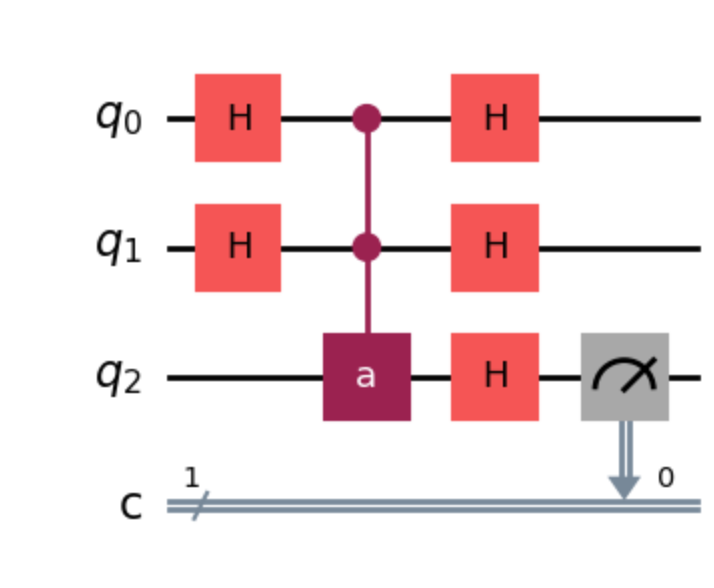
The Bernstein-Vazirani Problem and the Phase Estimation Problem
We have learned that applying the Hadamard gate to multiple input terminals allow quantum computers to handle multiple classical cases in one run. A classical example that demonstrates the use of this technique is the Deusch-Joza algorithm. Assuming that the oracle function is either constant or balanced, the algorithm allows Alice to deduce the type…
-
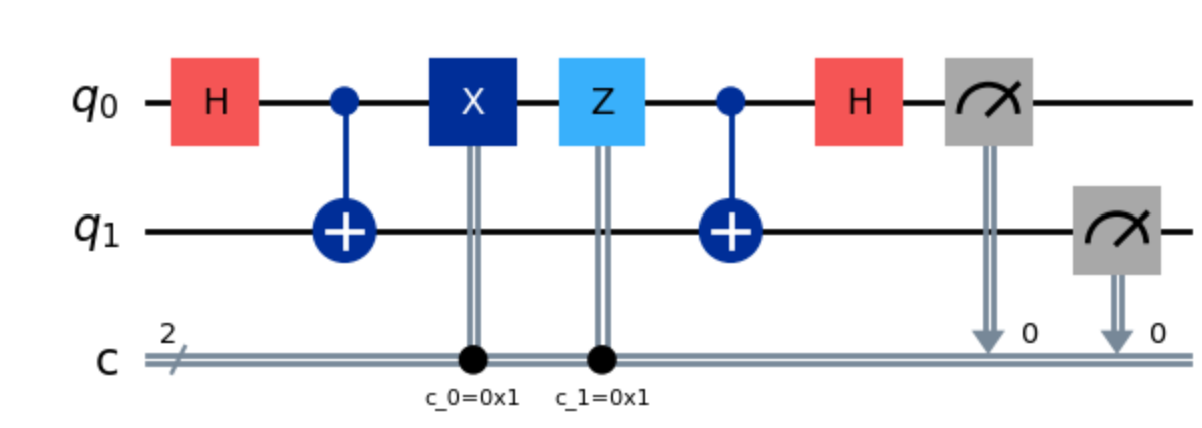
Superdense Coding and Quantum Teleportation
When studying quantum systems, we naturally seek the connection between classical systems. A natural discourse is to seek the link between classical bits and qubits. In particular, we seek the answers for two questions. First, is it possible to transfer a classical bit using a quantum channel? Second, is it possible to copy an arbitrary…
Got any book recommendations?