Category: Quantum Computing
-
Eigenvalue Estimation Algorithm
All quantum gates correspond to a unitary operator. In fact, this implies that all the eigenvalues of a quantum gate can be described in a form of a complex exponential of the form \[\lambda \ = \ e^{i\omega}. \] Here is a proof. Let \(U\) be the unitary operator for some quantum gate and consider…
-
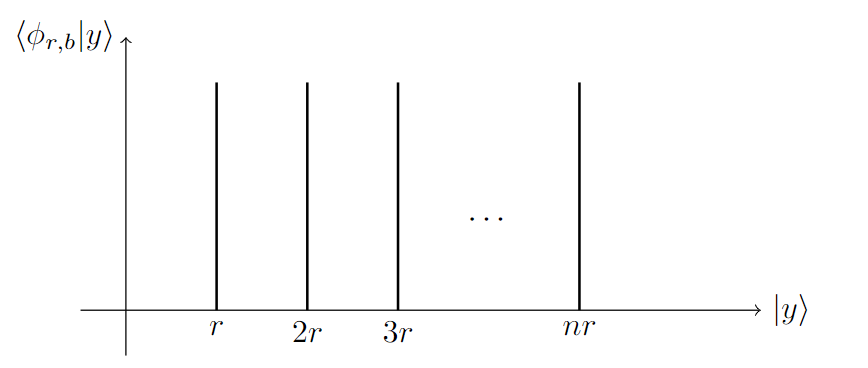
Periodic States and Period Testing
The machinery of quantum mechanics has a flavor of linear algebra and analysis. For example, quantum states exist within a Hibert space, and the Bloch sphere used to demonstrate a state of a 1-qubit system is a geometric object living in \(\mathbb R^3\). We wish to apply the abstract, continuous machinery in a discrete setting.…
-
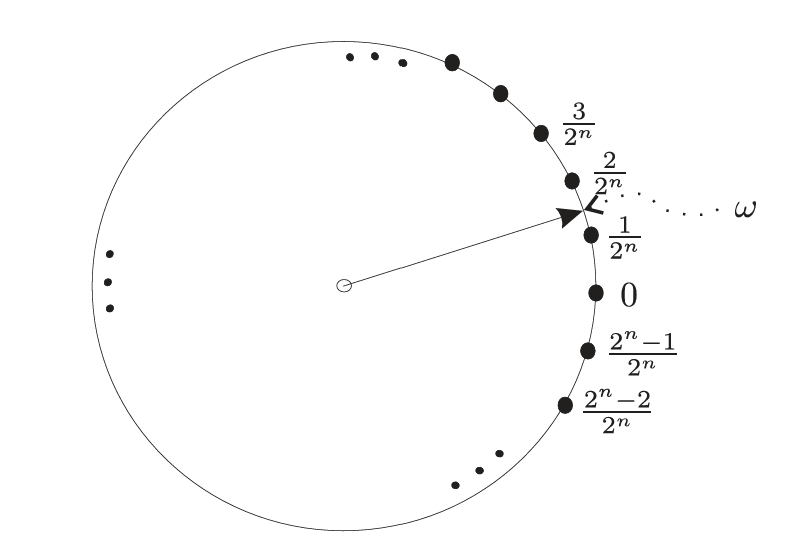
Phase Estimation for arbitrary phase
In the previous post, we explored the method of phase estimation where we recovered the phase factor \(\omega\) from the state \[ \frac 1 {\sqrt{m}}\sum_{y = 0}^{m} \exp(2 \pi i \omega y)|y\rangle \] and we demonstrated that a quantum circuit consisting of Hadamard gates and controlled rotations can recover the binary digits of \(\omega\) in…
-
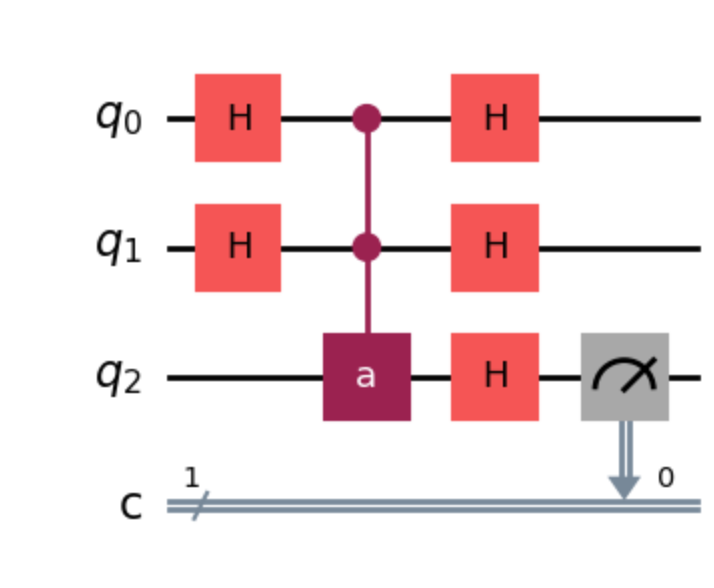
The Bernstein-Vazirani Problem and the Phase Estimation Problem
We have learned that applying the Hadamard gate to multiple input terminals allow quantum computers to handle multiple classical cases in one run. A classical example that demonstrates the use of this technique is the Deusch-Joza algorithm. Assuming that the oracle function is either constant or balanced, the algorithm allows Alice to deduce the type…
-
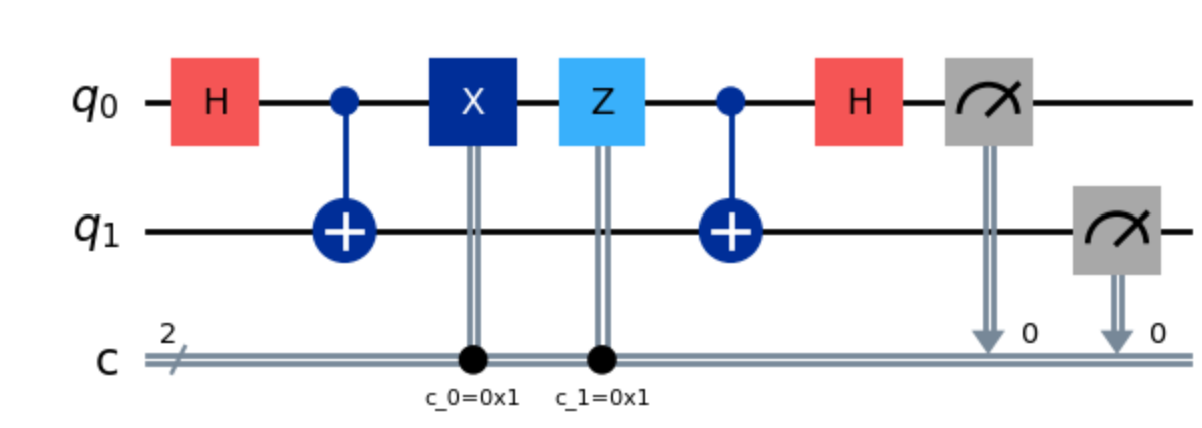
Superdense Coding and Quantum Teleportation
When studying quantum systems, we naturally seek the connection between classical systems. A natural discourse is to seek the link between classical bits and qubits. In particular, we seek the answers for two questions. First, is it possible to transfer a classical bit using a quantum channel? Second, is it possible to copy an arbitrary…